Don’t Let Bad Data Sink Your Business: Master These Metrics
July 25, 2024
Balance Sheet vs. Profit and Loss Statement: Are You Reading Them WRONG?
August 6, 2024Introduction
Effective budgeting and cash flow management are vital for the success and sustainability of small businesses. Proper financial management helps businesses anticipate future financial needs, manage expenses, and ensure they have enough liquidity to cover their obligations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the strategies and best practices for budgeting and managing cash flow, enabling small business owners to make informed financial decisions and achieve long-term success.
Understanding Budgeting for Small Businesses
Budgeting is the process of creating a plan to spend your money. This spending plan is called a budget. For small businesses, budgeting is crucial as it helps in allocating resources, setting financial goals, and measuring performance against those goals.
Definition of Budgeting
Budgeting involves forecasting income and expenses over a specific period, usually a year. This forecast helps businesses allocate their resources efficiently and plan for future financial needs.
Types of Budgets
- Operational Budget: Covers the day-to-day expenses of running a business.
- Capital Budget: Deals with long-term investments and major expenditures.
- Cash Flow Budget: Focuses on the inflows and outflows of cash to ensure liquidity.
Benefits of Budgeting
Financial Control
Budgeting provides a clear picture of where your money is going, helping you control your finances better. It ensures that you have enough funds for essential expenses and helps avoid overspending.
Forecasting
By predicting future income and expenses, budgeting allows businesses to prepare for upcoming financial needs and opportunities. This foresight is essential for strategic planning and growth.
Performance Measurement
Budgets set financial benchmarks that can be used to measure actual performance. Comparing budgeted figures with actual figures helps identify areas of improvement and success.
Steps to Create a Small Business Budget
Assessing Current Financial Situation
Begin by analyzing your current financial position. Review past financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Understand your income sources, regular expenses, and any existing financial obligations.
Setting Financial Goals
Determine what you want to achieve financially. Goals could include increasing revenue, reducing costs, expanding operations, or saving for future investments. Clear, measurable goals will guide your budgeting process.
Estimating Revenues and Expenses
Based on historical data and market research, estimate your future revenues and expenses. Consider seasonal trends, economic conditions, and industry benchmarks. Be realistic to ensure your budget is achievable.
Common Budgeting Methods
Zero-based Budgeting
In zero-based budgeting, every expense must be justified for each new period. This method starts from a “zero base,” and each function within an organization is analyzed for its needs and costs.
Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting uses the previous year’s budget as a base and makes adjustments for the new period. It’s simple and easy to implement but may perpetuate inefficiencies.
Activity-based Budgeting
This method allocates costs based on activities that drive costs. It helps in identifying cost drivers and managing them effectively.
Budgeting Tools and Software
Top Budgeting Tools
- QuickBooks: Popular for its comprehensive accounting and budgeting features.
- Xero: Known for its ease of use and integration with various apps.
- FreshBooks: Ideal for small businesses and freelancers.
- Wave: Free tool that offers essential budgeting features.
Benefits of Using Software
Using budgeting software automates many aspects of financial management, reduces errors, and saves time. It provides real-time insights and detailed reports that help in making informed decisions.
Monitoring and Adjusting Budgets
Regular Reviews
Conduct regular reviews of your budget to compare actual performance against your projections. This helps in identifying variances and understanding their causes.
Adjusting for Variances
When you identify significant variances, adjust your budget accordingly. This might involve cutting unnecessary expenses or re-evaluating your revenue projections.
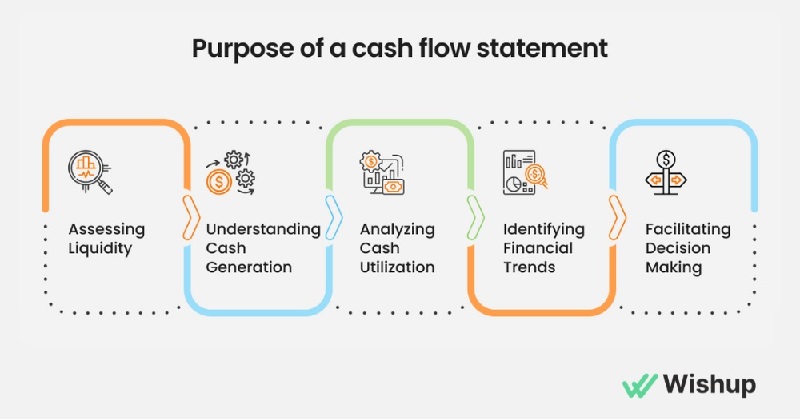
Understanding Cash Flow Management
Cash flow management involves tracking how much money is coming into and going out of your business. It ensures that your business has enough liquidity to meet its obligations.
Definition of Cash Flow
Cash flow is the net amount of cash being transferred into and out of a business. Positive cash flow indicates that a company’s liquid assets are increasing, enabling it to settle debts, reinvest, and cover expenses.
Importance of Cash Flow Management
Proper cash flow management ensures that a business can maintain sufficient cash reserves to cover its operational costs, invest in growth opportunities, and avoid financial distress.
Components of Cash Flow
Operating Activities
This includes all the cash transactions related to the core operations of the business, such as sales receipts, payments to suppliers, and wages.
Investing Activities
Cash flows from investing activities include the purchase and sale of assets like property, equipment, or securities.
Financing Activities
These are transactions involving the equity and debt of the business, such as issuing shares or borrowing funds.
Cash Flow vs. Profit
Differences Between Cash Flow and Profit
Profit is the amount of money left after all expenses have been deducted from revenue. Cash flow, on the other hand, refers to the actual inflows and outflows of cash. A business can be profitable but still face cash flow problems if revenues are not collected in a timely manner.
Why Both Are Important
While profit indicates the overall success of the business, cash flow ensures that the business has enough liquidity to sustain its operations.

Strategies for Managing Cash Flow
Improving Receivables
Accelerate the collection of receivables by invoicing promptly and offering incentives for early payments. Implement strict credit control measures to reduce late payments.
Managing Payables
Negotiate favorable payment terms with suppliers to improve cash outflows. Take advantage of early payment discounts when available.
Maintaining Cash Reserves
Establish a cash reserve to cover unexpected expenses and financial downturns. This helps in maintaining business continuity during challenging times.
Creating a Cash Flow Forecast
Steps to Create a Forecast
- Project Sales: Estimate future sales based on historical data and market analysis.
- Estimate Expenses: Predict future expenses, including fixed and variable costs.
- Analyze Cash Inflows and Outflows: Track when cash is expected to be received and when payments are due.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: Update your forecast regularly to reflect actual performance and changing conditions.
Tools for Cash Flow Forecasting
- Excel: Offers customizable templates for cash flow forecasting.
- Float: Provides real-time cash flow insights and integrates with accounting software.
- Futrli: Delivers advanced forecasting features and scenario planning.
Common Cash Flow Problems and Solutions
Identifying Cash Flow Issues
Common issues include late payments from customers, high levels of debt, and unforeseen expenses. Regular monitoring and analysis help in identifying these problems early.
Solutions to Improve Cash Flow
- Improve Credit Control: Implement stricter credit terms and follow up on overdue payments.
- Reduce Overheads: Cut unnecessary expenses to improve cash reserves.
- Increase Sales: Boost revenues through marketing and sales strategies.
Financing Options for Small Businesses
Types of Financing
- Bank Loans: Traditional loans from banks with fixed repayment terms.
- Lines of Credit: Flexible borrowing options with a credit limit.
- Invoice Financing: Borrowing against outstanding invoices.
- Equity Financing: Raising funds by selling shares of the business.
How to Choose the Right Option
Consider factors such as interest rates, repayment terms, and the impact on cash flow when selecting a financing option.
Using Credit Wisely
Managing Business Credit
Maintain a good credit score by paying bills on time and keeping debt levels manageable. Regularly review your credit report for accuracy.
Avoiding Debt Pitfalls
Avoid over-reliance on credit to fund operations. Use credit for strategic investments that generate returns, rather than covering operational shortfalls.
Emergency Funds for Small Businesses
Importance of Emergency Funds
An emergency fund provides a financial buffer during unforeseen circumstances, such as economic downturns or unexpected expenses.
How to Build an Emergency Fund
Set aside a portion of your profits regularly until you accumulate enough funds to cover at least three to six months of operating expenses.
Financial Ratios and Analysis
Key Financial Ratios
- Current Ratio: Measures liquidity by comparing current assets to current liabilities.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Assesses financial leverage by comparing total debt to shareholders’ equity.
- Gross Profit Margin: Indicates the profitability of core activities by comparing gross profit to revenue.
How to Use Ratios for Decision-Making
Use financial ratios to identify strengths and weaknesses in your financial performance. Ratios provide insights into liquidity, profitability, and solvency, aiding in strategic decision-making.
Case Studies of Successful Cash Flow Management
Real-World Examples
Explore case studies of small businesses that successfully managed their cash flow. Learn from their strategies, such as optimizing inventory levels, negotiating better payment terms, and improving cash collection processes.
Lessons Learned
Understand the key takeaways from these case studies, including the importance of proactive cash flow management and the impact of strategic financial planning.
Tips for Long-term Financial Planning
Setting Long-term Goals
Define clear, achievable long-term financial goals for your business. These goals should align with your overall business strategy and vision.
Strategies for Growth and Stability
Implement strategies to achieve long-term financial stability and growth. This might include diversifying revenue streams, investing in technology, and expanding your market presence.
Conclusion
Effective budgeting and cash flow management are essential for the success of small businesses. By understanding and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, business owners can ensure financial stability, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term growth. Remember, regular monitoring and adjustment of your financial plans are crucial to adapt to changing circumstances and opportunities.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between a budget and a cash flow statement?
- A: A budget is a financial plan that estimates future income and expenses over a specific period, usually a year. A cash flow statement, on the other hand, records the actual inflows and outflows of cash within the business over a period, providing a real-time view of liquidity.
Q: How often should I review my budget?
- A: It’s recommended to review your budget at least monthly. Regular reviews help you compare actual performance against your projections, identify variances, and make necessary adjustments.
Q: What are some common cash flow problems for small businesses?
- A: Common cash flow problems include late payments from customers, high levels of debt, unexpected expenses, and seasonal fluctuations in revenue.
Q: How can I improve my cash flow?
- A: Improve your cash flow by accelerating receivables, managing payables effectively, maintaining cash reserves, and reducing overhead costs. Additionally, regularly monitoring your cash flow and making necessary adjustments is crucial.
Q: What financing options are available for small businesses?
- A: Small businesses can explore various financing options, including bank loans, lines of credit, invoice financing, and equity financing. Each option has its advantages and considerations, so it’s important to choose the right one based on your business needs.
Q: Why is it important to have an emergency fund?
- A: An emergency fund provides a financial buffer during unforeseen circumstances, helping to ensure business continuity. It covers unexpected expenses and helps maintain operations during economic downturns or other financial challenges.
Conclusion
Effective budgeting and cash flow management are essential for the success of small businesses. By understanding and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, business owners can ensure financial stability, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term growth. Remember, regular monitoring and adjustment of your financial plans are crucial to adapt to changing circumstances and opportunities.
Resources
Financial Planning Tools for Small Businesses
- Manage Your Finances
Understanding Financial Ratios
- Financial Ratios
- Hot to Build an Emergency Fund
DISCLAIMER: The information in this article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to take the place of legal and accounting advice.