Future-Proof Your Business: A Step-by-Step Strategic Planning Process
November 12, 2024
Investing for Long-Term Success: Small Business Owners’ Guide to Building Wealth
December 15, 2024Financial forecasting plays a pivotal role in guiding businesses toward sustainability and growth. By leveraging past data, trends, and innovative tools, companies can predict their financial performance, allocate resources wisely, and prepare for uncertainties.
Introduction to Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting is the process of estimating a company’s future financial performance. It uses historical data, market trends, and assumptions to create a roadmap for decision-making.
This strategic tool is crucial for all businesses, regardless of size or industry, as it:
- Helps predict future opportunities and challenges.
- Aids in preparing for financial uncertainty.
- Strengthens investor and stakeholder confidence.
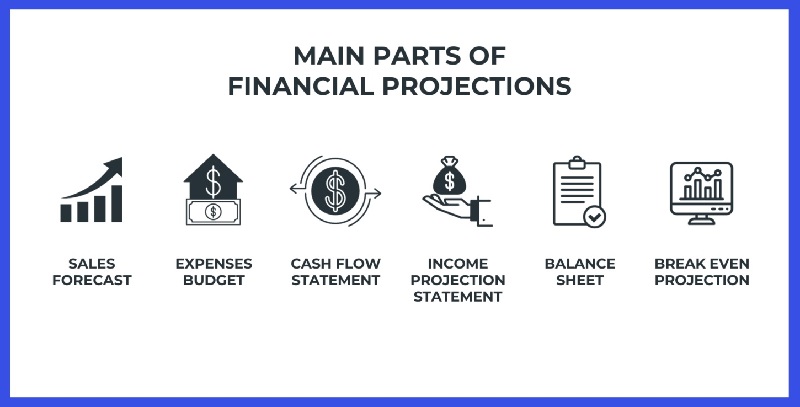
Key Elements of Financial Forecasting
The backbone of financial forecasting includes:
- Revenue: Estimating future income based on sales data and market trends.
- Expenses: Predicting costs, both fixed (rent, salaries) and variable (materials, utilities).
- Profits: Calculating potential earnings by subtracting costs from revenues.
- Cash Flow: Assessing cash movement to ensure liquidity and solvency.
Types of Financial Forecasting
Different forecasting methods cater to various business needs:
- Short-term Forecasting: Focused on immediate financial health, typically monthly or quarterly.
- Long-term Forecasting: Encompasses years and aligns with broader business objectives.
- Qualitative Forecasting: Uses expert opinions, market analysis, and industry insights.
- Quantitative Forecasting: Relies on statistical data, algorithms, and numerical models.
Benefits of Financial Forecasting
The advantages of financial forecasting include:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven insights for strategic choices.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies potential financial threats early.
- Investor Relations: Demonstrates preparedness and builds trust.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Ensures efficient use of financial assets.
Challenges in Financial Forecasting
Forecasting, while essential, has its obstacles:
- Data Limitations: Inaccurate or incomplete data can skew results.
- Market Volatility: Economic shifts or unexpected events disrupt projections.
- Assumption Errors: Unrealistic expectations may lead to over- or under-estimation.
Tools and Techniques for Financial Forecasting
Modern technology offers diverse solutions for accurate forecasting:
- Software Tools: QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks simplify forecasting.
- Statistical Techniques: Methods like trend analysis, regression, and moving averages.
- Financial Models: DCF (Discounted Cash Flow), scenario analysis, and what-if analysis.
Steps to Develop a Financial Forecast
Creating an effective financial forecast involves these key steps:
- Data Collection: Gather historical financial data and external market trends.
- Set Assumptions: Define variables like growth rates and operational costs.
- Build Models: Use spreadsheets or software to create predictive models.
- Validation: Compare forecasts to actual performance for accuracy.
Revenue Forecasting Methods
Predicting revenue requires a strategic approach:
- Bottom-Up Method: Starts with individual units (e.g., product or service) and scales up.
- Top-Down Method: Begins with market size and estimates the company’s share.
- Historical Analysis: Leverages past data to identify trends.
- Seasonality Adjustments: Accounts for seasonal fluctuations in sales.
Expense and Cost Forecasting
Accurate expense forecasting ensures budget stability:
- Fixed Costs: Rent, salaries, and insurance that remain constant.
- Variable Costs: Expenses like raw materials that fluctuate with production.
- Operational Costs: Day-to-day expenses critical to business functioning.
Utilizing benchmarks and historical data helps refine these estimates.
Cash Flow Forecasting
Maintaining a steady cash flow is vital for operational continuity. Cash flow forecasting predicts:
- Inflows: Revenue from sales, investments, and other income sources.
- Outflows: Payments for salaries, utilities, and vendor invoices.
A clear cash flow forecast prevents liquidity crises and supports timely decision-making.
The Role of Technology in Financial Forecasting
Technology has transformed financial forecasting:
- AI and Machine Learning: Analyze vast datasets for precise predictions.
- Predictive Analytics: Identify patterns and forecast trends.
- Cloud-Based Tools: Real-time collaboration and access to financial data.
These advancements enhance accuracy, save time, and improve adaptability.
Financial Forecasting for Startups vs. Established Businesses
Startups and established businesses face different forecasting challenges:
- Startups: Deal with limited historical data, rely on market research, and need agile forecasting.
- Established Businesses: Leverage extensive historical data and focus on refining operational efficiency.
Both require tailored forecasting strategies to meet their unique needs.
Scenario Planning in Forecasting
Scenario planning prepares businesses for varying outcomes:
- Best-Case Scenario: Projects maximum revenue and minimal costs.
- Worst-Case Scenario: Considers challenges like declining sales or rising expenses.
- Most Likely Scenario: Combines realistic assumptions for balanced projections.
This approach equips businesses to adapt to unexpected changes.
Common Mistakes in Financial Forecasting
Avoiding these pitfalls improves forecast accuracy:
- Over-Optimistic Projections: Unrealistic growth assumptions.
- Ignoring External Factors: Overlooking economic, political, or industry trends.
- Neglecting Updates: Failing to revise forecasts based on new data.
Regular reviews and conservative estimates can mitigate these errors.

Monitoring and Updating Financial Forecasts
Financial forecasting is not a one-time process. Continuous monitoring is essential:
- Periodic Reviews: Monthly or quarterly updates ensure relevance.
- Feedback Loops: Compare forecasts to actual performance and refine methods.
- Real-Time Adjustments: React swiftly to market changes or unexpected events.
Case Studies: Successful Financial Forecasting
Real-world examples highlight the value of accurate forecasting:
- Company A: Used advanced forecasting models to identify a growth opportunity, resulting in a 20% revenue increase.
- Company B: Mitigated risks by preparing for a market downturn, saving millions in potential losses.
These stories demonstrate the tangible impact of strategic forecasting.
Financial Forecasting for Future Trends
Businesses must forecast for evolving trends:
- Economic Shifts: Adapt to inflation, recession risks, or market recovery.
- Technological Advancements: Invest in AI and automation for competitive advantage.
- Industry Changes: Monitor regulatory changes and consumer behavior shifts.
Proactively addressing these trends ensures long-term resilience.
FAQs on Financial Forecasting
Q: How often should I conduct financial forecasting?
A: Businesses should update their forecasts at least quarterly or when major changes occur.
Q: Is financial forecasting essential for small businesses?
A: Absolutely. It helps small businesses plan effectively and secure funding.
Q: Can technology completely replace manual forecasting?
A: While technology enhances accuracy, human expertise is still critical for interpreting results.
Q: How do I forecast in uncertain markets?
A: Use scenario planning and conservative assumptions to prepare for multiple outcomes.
Q5: What’s the difference between budgeting and forecasting?
A5: Budgeting sets financial goals; forecasting predicts future performance based on current trends.
Q: Which software is best for forecasting?
A: Popular options include QuickBooks, Microsoft Excel, and specialized tools like Adaptive Insights.
Resources
Financial Forecasting Tools and Software
- Provides detailed information about tools like QuickBooks that streamline financial forecasting processes.
Understanding Cash Flow and Its Importance
- A comprehensive guide from Investopedia on cash flow, crucial for building accurate financial forecasts.
Benefits of Scenario Planning for Businesses
- This Harvard Business Review article discusses how scenario planning can prepare businesses for market uncertainties.
DISCLAIMER: The information in this article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to take the place of legal and accounting advice.