Learn Cash Flow Statement Essentials: Your Key to Financial Success!
October 28, 2024
Future-Proof Your Business: A Step-by-Step Strategic Planning Process
November 12, 2024Introduction to Self-Employed Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is crucial for everyone, but for self-employed individuals, it can be both a unique challenge and opportunity. Unlike traditional employees who often rely on employer-sponsored retirement plans, self-employed individuals must create their own retirement pathways. A variety of options—such as the Solo 401(k), Solo Roth 401(k), Roth IRA, and SEP IRA—cater specifically to these needs. Here, we’ll break down these top retirement plans, explore their benefits, eligibility requirements, and how each can help you achieve your retirement dreams.
Benefits of Retirement Plans for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement plans tailored for the self-employed offer numerous advantages, including tax benefits, wealth-building potential, and investment control. Contributing to these plans reduces taxable income, often allowing for significant tax savings. Moreover, they empower you with the freedom to diversify investments and optimize wealth accumulation according to your unique goals.
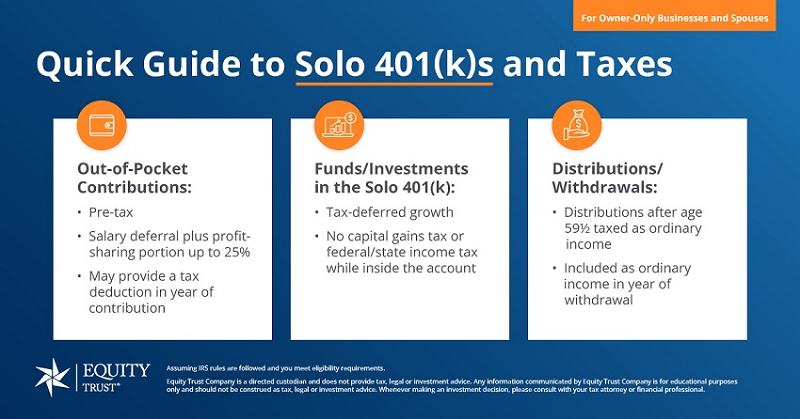
Understanding the Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k) is a retirement plan designed exclusively for self-employed individuals with no full-time employees (except a spouse). It combines the features of both traditional 401(k)s and profit-sharing plans, making it a popular choice for those seeking high contribution limits and flexibility. In 2024, the total contribution limit for Solo 401(k)s can reach up to $66,000 or $73,500 with catch-up contributions for those over 50.
Exploring the Solo Roth 401(k)
The Solo Roth 401(k) is similar to the Solo 401(k) but with one important difference: contributions are made post-tax rather than pre-tax. This means you pay taxes upfront but enjoy tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals during retirement. This structure can be particularly beneficial for younger individuals or those expecting to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
What is a Roth IRA?
A Roth IRA stands out for its tax-free growth and withdrawal benefits. Unlike traditional IRAs, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals are tax-free. Roth IRAs also provide flexibility with contribution limits based on income. In 2024, those with modified adjusted gross incomes of up to $153,000 (or $228,000 for married couples) can contribute the maximum amount.
Overview of the SEP IRA
The Simplified Employee Pension IRA (SEP IRA) is a favored option for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It allows for tax-deductible contributions up to 25% of compensation, with a cap at $66,000 for 2024. The SEP IRA is simple to establish, has fewer regulatory requirements, and permits higher contributions than traditional IRAs, making it an attractive choice for high-income earners seeking tax-deferred growth.
Solo 401(k) vs. Solo Roth 401(k)
Comparing the Solo 401(k) with the Solo Roth 401(k) often boils down to tax timing. If you prefer immediate tax deductions and expect a lower tax bracket in retirement, the Solo 401(k) is ideal. For those who foresee higher income in retirement, the tax-free withdrawals of a Solo Roth 401(k) might be more advantageous.
Solo 401(k) vs. SEP IRA
The Solo 401(k) and SEP IRA both offer high contribution limits and are flexible options for the self-employed. However, Solo 401(k)s permit both employer and employee contributions, while SEP IRAs limit contributions to employer contributions only. This distinction can influence your choice, particularly if you prioritize maximizing contributions.
Roth IRA vs. Solo Roth 401(k)
For individuals with fluctuating incomes or those who want additional tax-free growth, the Roth IRA offers lower contribution limits than the Solo Roth 401(k) but is available regardless of business status. By contrast, a Solo Roth 401(k) is best for self-employed individuals seeking higher contribution flexibility and the same tax-free growth benefits.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Plan
Each retirement plan comes with specific eligibility criteria. While the Solo 401(k) and SEP IRA are generally available to any self-employed person without employees, Roth IRAs come with income restrictions. It’s essential to understand these requirements to choose the plan that aligns best with your financial situation.
Contribution Limits for 2024
For 2024, each plan’s contribution limits differ significantly:
- Solo 401(k): $66,000 (or $73,500 with catch-up contributions)
- Solo Roth 401(k): Same limits as Solo 401(k)
- SEP IRA: Up to 25% of compensation, capped at $66,000
- Roth IRA: $6,500 (or $7,500 for those over 50)
Understanding these limits can help you maximize your contributions and tax savings each year.
Tax Advantages and Withdrawals
Retirement plans offer different tax benefits, such as tax-deferred or tax-free growth. However, early withdrawals before age 59½ typically incur penalties, except for Roth IRAs, which allow for the withdrawal of contributions penalty-free under certain conditions.
Investment Options Across Plans
These self-employed retirement plans provide various investment options. Solo 401(k)s and SEP IRAs generally permit a wide range of assets, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Roth IRAs offer similar flexibility, though certain restrictions apply based on the custodian.

Choosing the Right Plan Based on Income and Age
To decide on the most suitable retirement plan, consider both your current and anticipated income levels, along with your age and retirement goals. Young self-employed individuals may benefit more from a Solo Roth 401(k) or Roth IRA, while older individuals might prioritize tax deductions through a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k).
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes include underfunding, failing to plan for taxes, and missing important deadlines. A solid understanding of each plan’s rules and deadlines can help you avoid these pitfalls, maximizing your retirement savings efficiently.
FAQs on Self-Employed Retirement Plans
- Q: Can I have more than one retirement plan?
A: Yes, combining plans like a Solo 401(k) and Roth IRA is possible within contribution limits. - Q: What happens if I hire employees?
Hiring full-time employees may affect eligibility for certain plans like Solo 401(k). - Q: How does a Roth conversion work?
A: You can convert a Solo 401(k) to a Solo Roth 401(k) by paying taxes on the converted amount. - Q: How can I avoid penalties on withdrawals?
A: Withdrawals after age 59½ avoid penalties, and Roth IRAs allow for contributions to be withdrawn at any time. - Q: Which plan offers the most flexibility?
A: Solo 401(k)s generally offer the most flexibility for high contributions and investment choices.
Conclusion
Choosing the right retirement plan as a self-employed individual can secure financial stability and offer meaningful tax advantages. Whether you prefer the high contribution limits of a Solo 401(k), the tax-free growth of a Roth IRA, or the simplicity of a SEP IRA, each plan can help you build the retirement wealth you envision.
Resources
IRS rules for Solo 401(k) contributions
- IRS Guidelines for Solo 401(k) Plans
Roth IRA contribution limits and eligibility
- Contribution Limits and Eligibility for Roth IRAs
SEP IRA guidelines for small business owners
- Overview of SEP IRAs for Small Business Owners
DISCLAIMER: The information in this article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to take the place of legal and accounting advice.



